Prebiotics are a category of dietary fibers in certain foods which cannot be digested. These fibers move through the small intestine undigested and are fermented by the time they reach the colon, or large intestine. Prebiotics feed the beneficial bacteria colonies in the gut, including probiotic bacteria. Scientific studies have indicated that increasing prebiotic fiber supports our digestive and immune systems, bone density, weight management and brain health.
On the other hand, probiotics are a type of live, friendly bacteria that are naturally produced by the fermentation of certain foods. These help repopulate the colon with beneficial bacteria after taking antibiotics for a digestive illness. Antibiotics wipe out all bacteria, good and bad, so consuming probiotics is an important way to reset and balance your system.
Benefits of prebiotics
Prebiotics are a component of some foods that the body cannot digest. They serve as food for bacteria and other beneficial organisms in the gut. The benefits of prebiotics have links to the benefits of probiotics. Prebiotics may support a healthy gut, offering better digestive health, fewer antibiotic-related health problems, and other benefits. Prebiotics may benefit the body by:
- improving calcium absorption
- changing how quickly the body can process carbohydrates
- supporting the probiotic growth of gut bacteria, potentially enhancing digestion and metabolism
Prebiotics occur naturally in many foods, so there is no need for people to take prebiotic supplements.
Benefits and side effects of probiotics
It suggests that they may be beneficial in the following areas:
Digestive health: Numerous studies have found that probiotics may improve digestive health.
Mental health: A smaller body of research suggests that probiotics may improve mental health.
Gastrointestinal health: The results of studies generally suggest that people with disorders affecting the stomach and intestines may see improvements with probiotics.
General health: They found that probiotics may decrease:
- the need for antibiotics
- the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia
- gestational diabetes
- vaginal infections, such as yeast infections
- eczema
Side effects
People have a higher risk of adverse events when they take a specific probiotic. People with weakened immune systems were also more vulnerable to side effects.
PREBIOTICS Foods
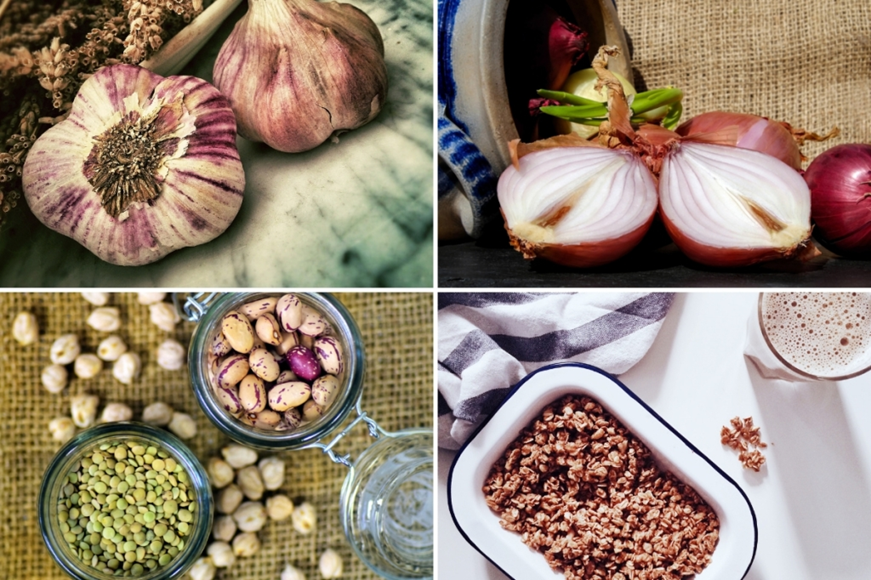

Chicory Root
With a coffee-like flavor, this root is popular in the southern USA as an alternative to coffee. It is packed with prebiotic fiber called inulin which nourishes the gut bacteria, enhances digestion, relieves constipation and increases bile production, which in turn improves fat digestion.
Onions
Raw onions offer organic sulfur compounds and contain Vitamin C and chromium to boost insulin production and protect you against free radicals. Peel off as little as possible before chopping or dicing. Cooked onions are also a high prebiotic food. Caramelize, fry, grill or sauté and enjoy this flavorful, healthy addition to your savory meal!
Raw Garlic
Chock full of nutrients, including manganese, Vitamin B6, Vitamin C, and selenium, garlic is a miracle food. To add raw garlic to your diet, make a habit of crushing a few cloves of it into the dish anytime you make guacamole, hummus, baba ganoush, vegetable stir fry or tomato sauce.
Oatmeal
Whole oats are a healthy grain that contain beta-glucan fiber and resistant starch. Consumption of oats has been shown to promote healthy gut bacteria, reduce LDL cholesterol, improve blood sugar control, reduce the risk of certain cancers, slow down digestion and help with appetite control.
Raw Dandelion Greens
Loaded with nutrients, such as Vitamin K, Vitamin A, calcium, and iron, raw dandelion greens can help with blood clotting and bone strength. Toss them into salads, sandwiches, soups or herbal teas. If needed, you can blanch them in boiling water for 30 seconds to reduce their slightly acrid taste.
Flax seeds
The fiber in flax seeds encourages the growth of healthy gut bacteria and promotes regularity. Integrating this healthy ingredient into your diet also assists by reducing the level of dietary fat digested and absorbed into the body. Flax seeds also have cancer preventing and antioxidant properties and help control blood sugar levels.
PROBIOTICS Foods

Yogurt
This is an excellent probiotic food, made from milk fermented by beneficial bacteria.
Eating yogurt can help improve bone health, lower blood pressure and relieve the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Be sure to consume yogurt with active or live cultures.
Kimchi
Kimchi is a Korean dish made of fermented cabbage and sometimes other fermented vegetables. It is a great source of vitamin K, vitamin B2 and iron. Kimchi has lactic acid bacterias that help improve the health of the digestive system. Its strong flavor is produced by an array of spices including red chili flakes, garlic, ginger, scallion and salt.
Miso
Miso is a Japanese seasoning made of fermented soybeans. Miso paste is the key ingredient in miso soup. It comes in several varieties, including white, yellow, red and brown. Miso is a good source of protein and fiber. Miso has been linked to a lower risk of breast cancer and reduced risk of stroke thanks to its high levels of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin K, manganese and copper.
Kefir
Kefir grains are cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeast. This super healthy, fermented probiotic milk drink is produced by adding kefir grains to cow or goat milk. Kefir is an even more potent source of probiotics than yogurt and can improve bone health, assist with digestive problems and prevent infections.
Kombucha
As any modern yogi knows, kombucha is a fermented tea drink. Made from green, white or black tea fermented by beneficial bacteria and yeast, it offers a myriad of digestive health benefits due to its probiotic properties.
Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is a stringent cabbage dish. Fermented by lactic acid bacteria, it will last for months in a closed container. In addition to its prebiotic and probiotic characteristics, sauerkraut is rich in vitamins C, B and K and contains iron and manganese, as well as antioxidants that assist eye health. Pasteurization kills active bacteria, so be sure to consume only non-pasteurized varieties.
Probiotics are friendly bacteria which help prevent disease due to harmful gut bacteria and fungi, while prebiotics are food for these and other types of beneficial bacteria that live in our intestines. To maintain optimal gut health, both are essential to incorporate into your daily diet.
Do you need probiotic and prebiotic supplements?
Probiotics are good bacteria in the gut that help fight against bad bacteria and external threats. With good fiber intake, consumption of fermented food, and yogurt, you do not need any probiotic supplementation. Prebiotics, which serves as food to probiotics and help them grow.
As a practical approach, supplementing may not be necessary for the person who is having a good fiber intake and also easily incorporates naturally occurring fermented food and yogurt. And, then though if one wishes to supplement the same, it is important to do it under the supervision of a doctor and only under specific gut related problems.
