A gluten-free diet involves excluding foods that contain the protein gluten, including wheat, rye and barley. Most studies on gluten-free diets have been done on people with celiac disease, but there is another condition called gluten sensitivity that also causes problems with gluten. If you are intolerant to gluten, then you need to avoid it completely. If not, you will experience severe discomfort and adverse health effects.
What Is Gluten?
Gluten is a family of proteins found in wheat, barley, rye and spelt. Its name comes from the Latin word for “glue,” as it gives flour a sticky consistency when mixed with water. This glue-like property helps gluten create a sticky network that gives bread the ability to rise when baked. It also gives bread a chewy and satisfying texture.
Unfortunately, many people feel uncomfortable after eating foods that contain gluten. The most severe reaction is called celiac disease. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the body mistakenly harms itself. Celiac disease affects up to 1% of the population and can damage the intestines. If eating gluten makes you feel uncomfortable, it’s best to not eat gluten foods.
Why Gluten Is Bad for Some People
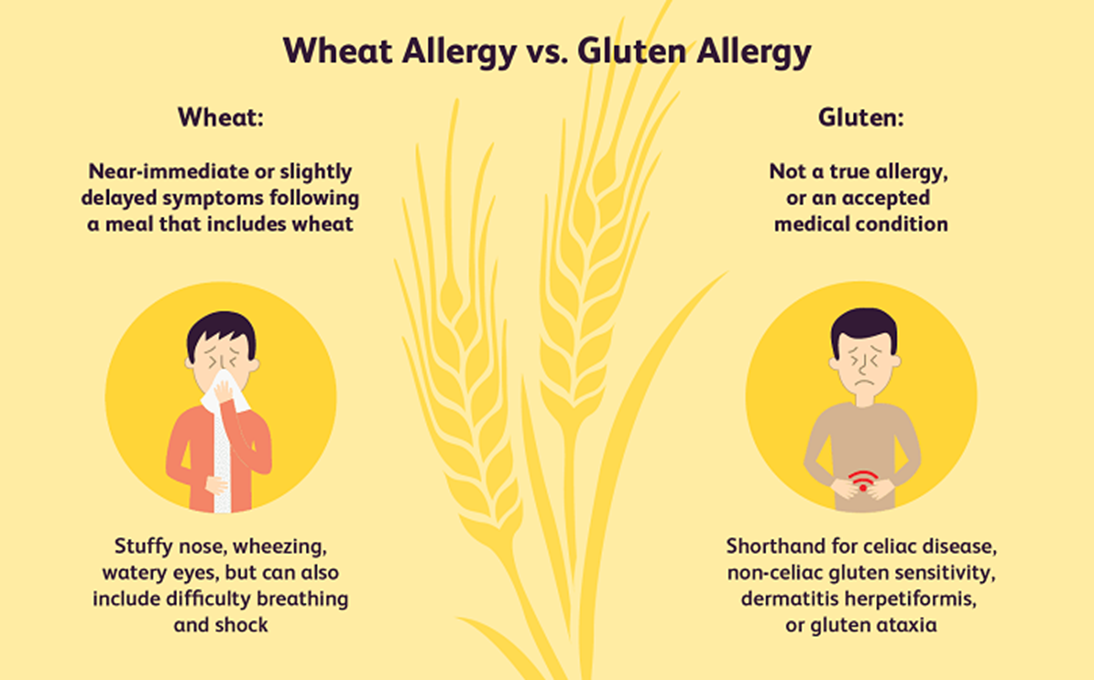
People with other disorders like wheat allergy and non-celiac gluten sensitivity also frequently avoid gluten. Aside from an allergy, there are two main reasons why someone would want to avoid gluten.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease affects up to 1% of people worldwide. It is an autoimmune disease in which the body mistakes gluten as a foreign threat. To remove this “threat,” the body overreacts and attacks the gluten proteins.
Unfortunately, this attack also damages surrounding areas, such as the gut wall. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, severe digestive issues and anemia, as well as increase the risk of many harmful diseases.
People with celiac disease often experience sharp stomach pain, diarrhea, constipation, skin rashes, stomach discomfort, bloating, weight loss, anemia, tiredness and depression. Interestingly, some people with celiac disease don’t experience digestive symptoms. Instead, they may experience other symptoms like fatigue, depression and anemia.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity is believed to affect 0.5–13% of people. People who are classified as having non-celiac gluten sensitivity do not test positive for celiac disease or a wheat allergy. However, they still feel uncomfortable after eating gluten.
Symptoms of non-celiac gluten sensitivity are similar to those of celiac disease and include stomach pain, bloating, changes in bowel motions, tiredness and eczema or a rash. However, non-celiac gluten sensitivity is highly controversial. Some experts believe this sensitivity exists, while others believe it is all in people’s heads.
For example, one study tested this theory on 35 people with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Scientists gave participants both a gluten-free flour and a wheat-based flour at separate times without identifying them.

A gluten-free diet has many benefits, especially for someone with celiac disease. Here are the main benefits of a gluten-free diet.
May Relieve Digestive Symptoms
Most people try a gluten-free diet to treat digestive problems. These include bloating, diarrhea or constipation, gas, fatigue and many other symptoms. Studies have shown that following a gluten-free diet can help ease digestive symptoms for people with celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
In one study, 215 people with celiac disease followed a gluten-free diet for six months. The diet helped significantly reduce stomach pain and the frequency of diarrhea, nausea and other symptoms.
Can Reduce Chronic Inflammation in Those with Celiac Disease
Inflammation is a natural process that helps the body treat and heal infection. A gluten-free diet can help reduce chronic inflammation in those with celiac disease.
People with non-celiac gluten-sensitivity may also have low levels of inflammation. However, it’s not completely clear if a gluten-free diet can reduce inflammation in these people.
May Boost Energy
People with celiac disease often feel tired, sluggish or experience “brain fog”. These symptoms may be caused by nutrient deficiencies because of damage to the gut. For example, an iron deficiency can lead to anemia, which is common in celiac disease.
If you have celiac disease, switching to a gluten-free diet may help boost your energy levels and stop you from feeling tired and sluggish. In a study including 1,031 people with celiac disease, 66% of them complained of fatigue. After following a gluten-free diet, only 22% of people still experienced fatigue.
Can Help You Lose Weight
It’s not unusual to lose weight when you start following a gluten-free diet. This is because it eliminates many junk foods that add unwanted calories to the diet. These foods are often replaced by fruit, veggies and lean proteins.
However, it’s important to avoid processed “gluten-free” foods like cakes, pastries and snacks, as they can quickly add a lot of calories to your diet. Focus on eating plenty of whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, veggies and lean proteins
