In the realm of essential vitamins, Vitamin B12 stands out as a vital nutrient crucial for various bodily functions. Its role in energy production, nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation underscores its significance in maintaining overall health and well-being. However, despite its importance, many individuals may not be aware of the potential consequences of a Vitamin B12 deficiency or how to ensure an adequate intake through food sources. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the benefits of Vitamin B12, its food sources, deficiency symptoms, and treatment options.

Understanding Vitamin B12:
- What is Vitamin B12?
- Importance of Vitamin B12 for the body
- Role in energy metabolism
- Influence on neurological function
- Contribution to DNA synthesis and cell division
Benefits of Vitamin B12:
- Energy production and metabolism: Exploring how Vitamin B12 aids in converting food into energy, thereby preventing fatigue and promoting vitality.
- Cognitive function: Discussing the role of Vitamin B12 in maintaining neurological health, improving memory, and reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Red blood cell formation: Highlighting how Vitamin B12 contributes to the synthesis of red blood cells, thus preventing anemia and enhancing oxygen transport.
- Heart health: Exploring the potential links between Vitamin B12 deficiency and cardiovascular risks, including elevated homocysteine levels.
Food Sources of Vitamin B12:
- Animal-derived sources: Listing various foods rich in Vitamin B12 such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products.
- Plant-based sources: Discussing the challenges faced by vegetarians and vegans in obtaining adequate Vitamin B12 and exploring fortified foods and supplements as alternatives.
- Nutritional yeast: Highlighting nutritional yeast as a vegan-friendly source of Vitamin B12, commonly used as a cheese substitute in plant-based diets.
- Fermented foods: Exploring the presence of Vitamin B12 in fermented foods like tempeh, miso, and certain types of algae.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
- Causes of Vitamin B12 deficiency: Identifying factors such as inadequate dietary intake, malabsorption disorders, gastrointestinal surgeries, and certain medications.
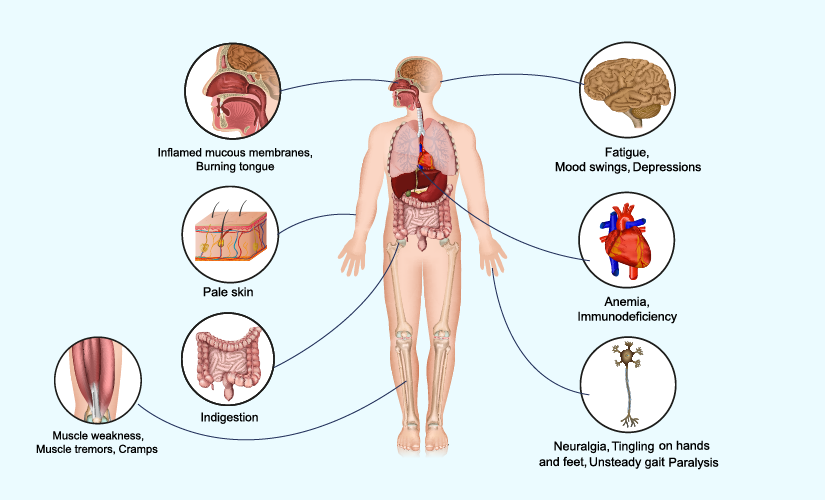
- Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency: Enumerating common signs such as fatigue, weakness, tingling sensations, cognitive impairment, and megaloblastic anemia.
- At-risk populations: Discussing groups more susceptible to Vitamin B12 deficiency, including older adults, vegetarians, vegans, and individuals with gastrointestinal disorders.
- Long-term consequences: Exploring the potential health complications associated with untreated Vitamin B12 deficiency, including neurological disorders and irreversible nerve damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency:
- Diagnostic tests: Describing laboratory tests such as serum Vitamin B12 levels, complete blood count (CBC), and methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels used to diagnose Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Treatment options: Discussing approaches to treating Vitamin B12 deficiency, including oral supplementation, intramuscular injections, and dietary modifications.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Highlighting the importance of regular monitoring to assess the effectiveness of treatment and prevent recurrence of deficiency symptoms.
- Addressing underlying causes: Emphasizing the need to identify and address underlying factors contributing to Vitamin B12 deficiency, such as gastrointestinal disorders or medication-induced malabsorption.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
- Dietary strategies: Offering practical tips for ensuring an adequate intake of Vitamin B12 through dietary sources, supplementation, or fortified foods.
- Lifestyle modifications: Recommending lifestyle changes to support Vitamin B12 absorption and utilization, such as reducing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking.
- Education and awareness: Advocating for increased awareness about Vitamin B12 deficiency and its implications, particularly among at-risk populations and healthcare professionals.
- Regular screenings: Encouraging routine screening for Vitamin B12 levels, especially for individuals with predisposing factors or symptoms suggestive of deficiency.
Vitamin B12 plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal health and well-being, influencing various physiological processes ranging from energy metabolism to neurological function. Understanding the benefits of Vitamin B12, identifying food sources rich in this essential nutrient, recognizing the symptoms of deficiency, and seeking appropriate diagnosis and treatment are crucial steps in safeguarding against potential health complications. By prioritizing adequate Vitamin B12 intake and addressing any underlying factors contributing to deficiency, individuals can take proactive measures to support their overall health and vitality.
