Surprise: Everyone has some belly fat, even people who have flat abs. That’s normal. But too much belly fat can affect your health in a way that other fat doesn’t. Some of your fat is right under your skin. Another fat is deeper inside, around your heart, lungs, liver, and other organs. It’s that deeper fat called “visceral” fat that may be the bigger problem, even for thin people.
Excess belly fat is extremely unhealthy. It’s a risk factor for diseases like metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Losing abdominal fat, or belly fat is a common weight loss goal. Abdominal fat is a particularly harmful type. For this reason, losing this fat can have significant benefits for your health and well-being.

What’s behind belly fat
Women tend to carry more fat around the lower abs/ hips and thighs just because of biology. A women’s body is designed to carry an offspring and the extra layer of fat around the belly will help you carry a baby safely.
Men tend to carry a layer of fat around the lower back instead because through generations men worked in agriculture and outdoors and an extra layer of fat around the lower back is protective and helpful to work long hours with a bent back.
Your weight is largely determined by three main factors:
· How many calories you consume during the day
· How many calories you burn off through daily exercise
· Your age
If you eat too much and exercise too little, you’re likely to carry excess weight — including belly fat. Also, your muscle mass might diminish slightly with age, while fat increases. Loss of muscle mass also decreases the rate at which your body uses calories, which can make it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight. The tendency to gain or carry weight around the waist — and have an “apple” rather than a “pear” shape — might have a genetic component as well.
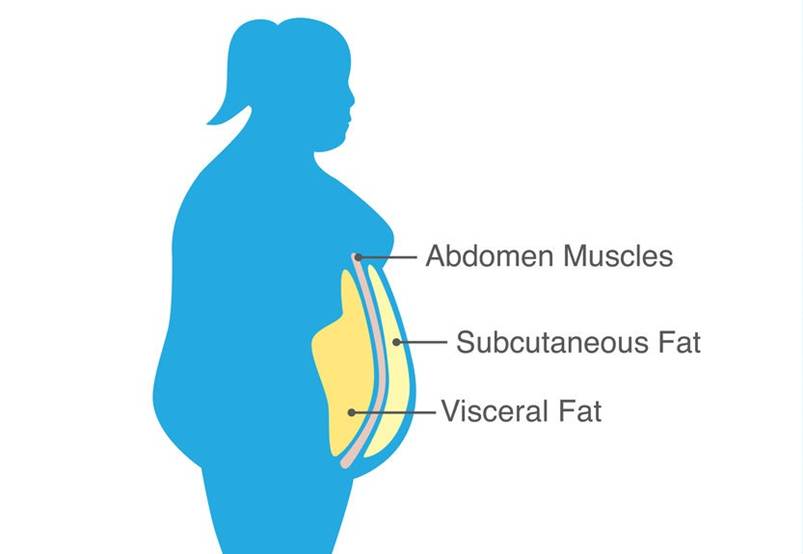
Why belly fat is more than skin deep
The trouble with belly fat is that it’s not limited to the extra layer of padding located just below the skin (subcutaneous fat). It also includes visceral fat — which lies deep inside your abdomen, surrounding your internal organs.
Although subcutaneous fat poses cosmetic concerns, visceral fat is linked with far more dangerous health problems, including:
· Heart disease
· Type 2 diabetes
· High blood pressure
· Abnormal cholesterol
· Breathing problems
Research also associates belly fat with an increased risk of premature death — regardless of overall weight.
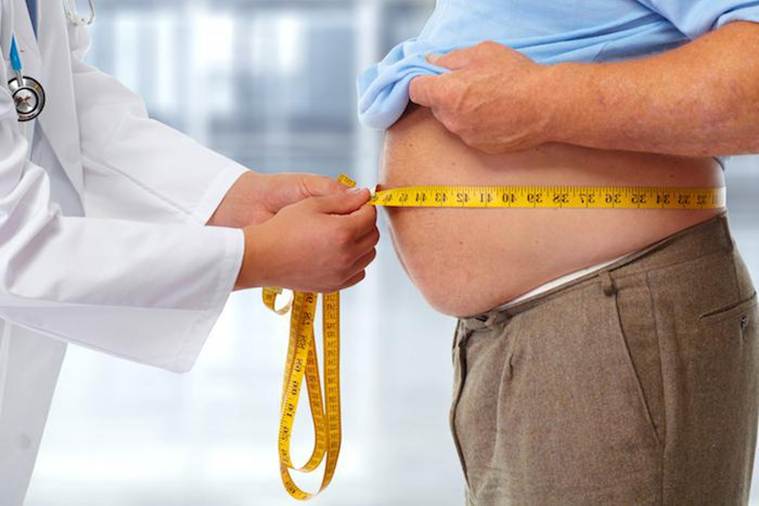
Measuring your middle
So how do you know if you have too much belly fat? Measure your waist:
· Stand and place a tape measure around your bare stomach, just above your hipbone.
· Pull the tape measure until it fits snugly around you, but doesn’t push into your skin. Make sure the tape measure is level all the way around.
· Relax, exhale and measure your waist, resisting the urge to suck in your stomach.
For women, a waist measurement of more than 35 inches (89 centimeters) and for men 40 inches (102 cm) indicates an unhealthy concentration of belly fat and a greater risk of health problems.

Trimming the fat
You can tone abdominal muscles with crunches or other targeted abdominal exercises, but just doing these exercises won’t get rid of belly fat. However, visceral fat responds to the same diet and exercise strategies that help you shed excess pounds and lower your total body fat. To battle belly fat:
Eat a healthy diet.
Focus on plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and choose lean sources of protein and low-fat dairy products. Limit added sugar and saturated fat, which is found in meat and high-fat dairy products, such as cheese and butter. Choose moderate amounts of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats — found in fish, nuts and certain vegetable oils — instead.
Replace sugary beverages.
Drink water or beverages with artificial sweetener instead.
Keep portion sizes in check.
Even when you’re making healthy choices, calories add up. At home, slim down your portion sizes. In restaurants, share meals — or eat half your meal and take the rest home.
Include physical activity in your daily routine.
For most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends moderate aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, for at least 150 minutes a week or vigorous aerobic activity, such as running, for at least 75 minutes a week.If you use a step counter, remember that it takes an average of 10,000 steps a day to prevent weight gain. Some studies indicate it might take 15,000 steps a day to prevent the regain of weight after significant weight loss. Strength training exercises also are recommended at least twice a week. If you want to lose weight or meet specific fitness goals, you might need to exercise more.
To lose excess fat and keep it from coming back, aim for slow and steady weight loss. Consult with us for getting started and staying on track.
