The body stores fat in many areas for energy and insulation. The liver partially consists of fat. However, if the fat content in the liver is too high, this may be a sign of fatty liver disease. Dietary changes are the first-line treatment for this liver condition.
The fatty liver disease damages the liver, preventing it from removing toxins and producing bile for the digestive system. When the liver cannot perform these tasks effectively, it puts a person at risk of developing other problems throughout their body. Dietary changes and regular exercise are key ways to manage fatty liver disease. Almost a third of our population suffers from fatty liver ailments. Here are some diet tips to minimize the risk.
Fatty liver disease is more common than ever. Most people associate fatty liver with drinking too much alcohol, but this common disease can also occur in people who don’t drink any alcohol at all. It is most common in people over the age of 60, however; it can occur in children and young adults. This form of fatty liver disease is called “Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease” or “NAFLD”. Unfortunately, Fatty Liver Disease can lead to chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease.
Top Causes of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

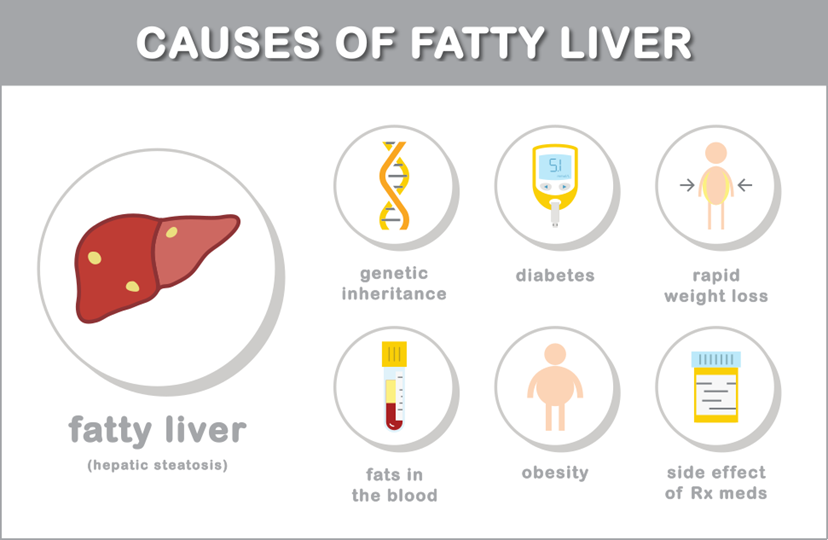
There are a whole range of reasons why someone might develop Fatty Liver Disease. Some causes like food intake and nutrition can be controlled; others, like pre-diabetes, have a genetic link that may not be as easily controlled and may require medication.
· Malnourishment – Malnutrition can cause mitochondrial changes which can lead to NAFLD.
· Obesity – Similar to malnutrition, overfeeding can cause inflammation which can affect liver function. It was found that the majority of obese adults have some form of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
· Pre-diabetes – Those who have a sensitivity to sugar or are insulin resistant will tend to have more fat and will store more fat in their liver than those who do not have pre-diabetes.
· Over-consumption of carbs and sugar – Too much sugar, refined carbs like white flour and soda has been linked to NAFL especially if these types of foods are consumed by insulin resistant individuals.
· Poor Gut Health – An imbalance of bacteria in the gut lining could contribute to the development of NAFLD in certain people.
· Genetics – Certain cultural groups are more prone to developing fatty liver especially men of Hispanic or African-American descent.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Most people don’t know that they have a fatty liver until the symptoms get more intense. Here are some common, early symptoms of Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease to watch out for:
· General fatigue
· A feeling of fullness in the right side or center of the abdomen
· A swollen belly
· Visible, enlarged blood vessels under the skin
· Reddish palms
· A yellow tinge to the skin and eyes
· Elevated liver enzymes
The most common early symptoms of NAFLD are a feeling of tiredness and slight pain in the right side of the abdomen. If you are experiencing 2 or more of the symptoms listed above, be sure to book an appointment with your doctor.
Foods to eat for a fatty liver
A diet for fatty liver disease should include a wide variety of foods. Reducing calorie intake and eating high-fiber, natural foods is a good starting point. Eating foods that contain complex carbohydrates, fiber, and protein can provide sustained energy and promote satiety.
Foods that reduce inflammation or help the body repair its cells are equally important. Some people choose to follow specific diet plans, such as a plant-based diet or the Mediterranean diet. A dietitian can often help a person create a customized diet plan that is right for their tastes, symptoms, and health status.
In addition to these basic guidelines, some specific foods may be especially helpful for people with fatty liver disease. These foods include:
Garlic
Garlic is a staple in many diets, and it may provide benefits for people with fatty liver disease. Garlic powder supplements appear to help reduce body weight and fat in those who have fatty liver disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids
A 2016 review of current research suggests that consuming omega-3 fatty acids improves the levels of liver fat and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Although more research is necessary to confirm this finding, eating foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids may help lower liver fat. These foods include:
· salmon
· sardines
· walnuts
· flaxseed
Coffee
Drinking coffee is a morning ritual for many people. However, it may provide benefits beyond a burst of energy for people with fatty liver disease.
A 2019 animal study Trusted Source found that decaffeinated coffee reduced liver damage and inflammation in mice that ate a diet containing high levels of fat, fructose, and cholesterol. The researchers found that coffee reduced the amount of fat that built up in the mice’s livers and improved how their bodies metabolized energy.
Broccoli
Eating a variety of whole vegetables is helpful for people with fatty liver disease. However, broccoli is one vegetable that a person with fatty liver disease should seriously consider including in their diet.
A 2016 animal study in The Journal of Nutrition found that the long-term consumption of broccoli helped prevent the buildup of fat in murine livers.
Researchers still need to conduct further studies involving humans. However, early research into the effect of broccoli consumption on the development of fatty liver disease looks promising.
Green tea
Using tea for medicinal purposes is a practice that goes back thousands of years.
A 2015 review in the World Journal of Gastroenterology suggests that green tea may help lower levels of fat in the blood and throughout the body. One of the included studies reported reduced levels of fat in the liver in people who consumed 5–10 cups of green tea per day.
Green tea provides several antioxidants, such as catechin, which may help improve fatty liver disease.
While all tree nuts are a great addition to any diet plan, walnuts are especially high in omega-3 fatty acids and may provide benefits for people with fatty liver disease.
Walnuts
A review from 2015 found that eating walnuts improved liver function test results in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Soy or whey protein
A 2019 review trusted Source in the journal Nutrients found that both soy and whey protein reduced fat buildup in the liver.
The results of one study in the review showed that liver fat decreased by 20% in women with obesity who ate 60 grams of whey protein every day for 4 weeks. Soy protein contains antioxidants called isoflavones that help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the levels of fats in the body.
Foods to avoid
Adding healthful foods to the diet is one way to manage fatty liver disease. However, it is just as important for people with this condition to avoid or limit their intake of certain other foods.
Sugar and added sugars
Added sugars contribute to high blood sugar levels and can increase fat in the liver.
Manufacturers often add sugar to candy, ice cream, and sweetened beverages, such as soda and fruit drinks.
Added sugars also feature in packaged foods, baked goods, and even store-bought coffee and tea. Avoiding other sugars, such as fructose and corn syrup, can also help minimize fat in the liver.
Alcohol
Alcohol is the most common cause of fatty liver disease. Alcohol affects the liver, contributing to fatty liver disease and other liver diseases, such as cirrhosis.
A person with fatty liver disease should reduce their intake of alcohol or remove it from their diet altogether.
Refined grains
Processed and refined grains are present in white bread, white pasta, and white rice. Producers have removed the fiber from these highly processed grains, which can raise blood sugar as the body breaks them down.
People can easily replace refined grains with potatoes, legumes, or whole-wheat and whole-grain alternatives.
Fried or salty foods
Too much fried or salty food is likely to increase calorie intake and the risk of weight gain. Obesity is a common cause of fatty liver disease.
Adding extra spices and herbs to a meal is a great way to flavor foods without adding salt. People can also usually bake or steam foods instead of frying them.
Meat
A 2019 review articleTrusted Source notes that saturated fat intake increases the amount of fat that builds up around organs, including the liver.
